The Ultimate Guide to Compression Springs
Introduction to Compression Springs

For over 30 years, ChinaCustomSpring has stood at the forefront of precision compression spring manufacturing, delivering engineered-to-perfection solutions to industries worldwide. As a professional compression spring manufacturer based in China, we combine state-of-the-art technology with three decades of specialized expertise to produce ultra-reliable, high-performance springs that not only meet the most stringent industry standards but exceed expectations in even the most demanding application-specific requirements.
Compression springs serve as the backbone of countless mechanical systems, offering unparalleled force resistance and energy storage capabilities. These precision-engineered helical wonders are integral to a vast range of mission-critical applications—from high-accuracy medical instruments and next-generation automotive suspensions to cutting-edge aerospace mechanisms and rugged heavy industrial equipment—making them one of the most universally relied-upon components in modern engineering.
What is a Compression Spring?
A compression spring is a helical coil made of round spring wire, featuring adjacent coils with a specific pitch that determines its length. Designed to operate under compressive loads, these springs store and release elastic energy when compressed. They also serve to absorb shock or maintain force between two surfaces. As the name implies, compression springs compress under an applied load, storing energy before returning to their original length once the force is removed. Their helical coil structure enables them to resist compressive forces, making them essential in various mechanical systems.
Compression springs are widely used across industries, from automotive suspensions and medical devices to robotics and everyday electronics like keyboards. These versatile helical components play a critical role in applications ranging from AI-driven robots to advanced medical technology.
At Compression Spring, our mission is to provide makers, inventors, and professionals with comprehensive knowledge about compression springs—from their fundamental mechanics to their intricate physical and mathematical properties. We explore key calculations, including spring rate, load capacity, loaded height, and dimensional specifications, along with material selection and relevant formulas. Our goal is to equip you with an in-depth understanding of compression springs and their applications.
Detailed Technical Specifications
- Wire Diameter
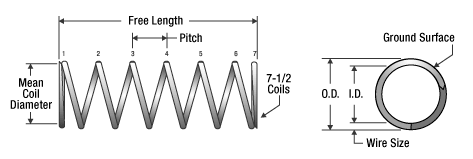
Wire Diameter: The diameter of the spring wire, measured from one side of the wire to the opposite side. - Outer Diameter
Outer Diameter: The external diameter of a compression spring, measured from one outer edge to the opposite outer edge. - Mean Coil Diameter
Mean Coil Diameter: The average diameter of the spring coils, calculated as the midpoint between the outer and inner diameters. The most accurate method to determine the mean diameter is to either subtract one wire diameter from the outer diameter or add one wire diameter to the inner diameter. This value is essential for calculating spring rate and stress in a compression spring. - Inner Diameter
Inner Diameter: The internal diameter of a compression spring, measured from one inner edge to the opposite inner edge. - Free Length
Free Length: The total length of a compression spring in its uncompressed state, also referred to as spring length or overall length. - Total Coils
Total Coils: The complete count of helical coils in a compression spring, including both pitched and non-pitched coils. - Active Coils
Active Coils: The number of helical coils that have pitch and contribute to energy exertion when the spring is compressed. - Solid Height
Solid Height: The compressed height of a spring when all coils are in contact, preventing further compression. Also known as coil bind height, this occurs when the spring can no longer exert force. - Compression Spring Rate Definition
Compression Spring Rate Definition: The spring rate (k) or spring constant represents the ratio of force (in pounds or newtons) to displacement (in inches or millimeters). This constant helps determine the required load for a given compression distance or predict compression travel under a specific load.
The Physics Behind Compression Spring Operation
Fundamental Principles of Spring Mechanics
Compression springs operate according to Hooke’s Law of Elasticity, which mathematically describes the linear relationship between force and displacement:
F = -k \cdot x
Where:
- F represents the applied force (measured in Newtons or pounds-force)
- k denotes the spring constant or spring rate (stiffness coefficient)
- x indicates the displacement distance (in millimeters or inches)
Critical Factors Affecting Spring Performance
The spring rate (k) is determined by four primary variables:
- Wire diameter (d): Increasing wire thickness exponentially increases stiffness (d⁴ relationship)
- Mean coil diameter (D): Larger diameters decrease spring rate (inverse cubic relationship)
- Number of active coils (n): More coils result in lower spring rates
- Material modulus of rigidity (G): Intrinsic material property affecting elasticity
The precise mathematical relationship is expressed as:
k = \frac{G \cdot d^4}{8 \cdot D^3 \cdot n}
Load-Deflection Behavior and Operational Limits
For optimal performance and longevity, compression springs should operate within 20% to 80% of their maximum deflection capacity. The test load (Fs) represents the maximum force a spring can withstand before experiencing permanent deformation:
Fs = \frac{\pi \cdot d^3 \cdot \tau}{8 \cdot D}
Where τ represents the allowable shear stress for the specific material.
Advanced Compression Spring Design Engineering
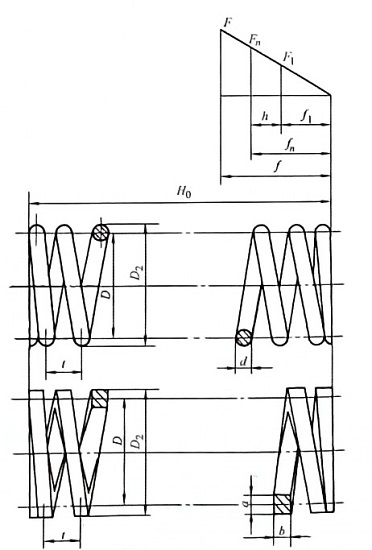
Comprehensive Geometric Parameters
| Parameter | Symbol | Measurement | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wire Diameter | d | mm/in | Directly affects strength and stiffness |
| Mean Diameter | D | mm/in | Determines space requirements and spring index |
| Free Length | L0 | mm/in | Unloaded spring dimension |
| Solid Length | Ls | mm/in | Fully compressed length (theoretical) |
| Pitch | p | mm/in | Distance between adjacent coils |
| Spring Index | C = D/d | Ratio | Critical for manufacturability and stress distribution |
Understanding Compression Spring End Types
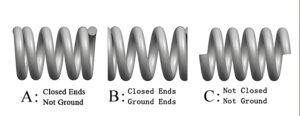
Selecting the appropriate compression spring end type is essential for optimal performance and fit within an assembly. Below are the most widely used end configurations.
-
Closed and Squared Ends
This design features a flat surface without additional grinding, making it ideal for springs with a slenderness ratio below 3.5. The squared ends enhance stability, preventing buckling under load. Recommended for applications requiring vertical alignment without external support.
-
Closed and Ground Ends
Grinding the spring ends produces a flatter, more precise surface, improving load distribution. Preferred for high-precision applications—such as automotive and industrial machinery—where consistent compression is critical. Best suited for springs with a slenderness ratio exceeding 4.
-
Open Ends
Open-end springs retain their natural, unmodified coil shape, resulting in slightly uneven ends. Their key advantage is increased travel distance, as they eliminate dead coils, maximizing usable space. A cost-effective choice when exact end alignment is unnecessary.
-
Double Closed Ends
This variation features two closed (but unground) ends, improving vertical rigidity and resistance to lateral movement. Ideal for assemblies where minimal guidance is available, though it reduces available solid height in exchange for stability.
-
Triple or More Closed Ends
A specialized design for fine-wire springs (0.005″–0.025″ diameter) with a large spring index. Multiple closed ends prevent instability during compression, ensuring reliable performance in delicate applications.
-
Multiple Closed Ends on One Side
This configuration allows the spring’s inner diameter to thread onto a bolt or shaft. Critical for secure assembly, the wire diameter and inner spring dimensions must match the thread specifications precisely.
-
One Closed End and Multiple Closed Ends
Combining a single closed end with multiple closed ends on the opposite side enhances base stability while maintaining a flat top surface. Optional grinding further refines contact precision for demanding applications.
Spring Index (C) Optimization
- Low C Values (3-6):
- High stress concentration
- Difficult manufacturing process
- Excellent for space-constrained applications
- Medium C Values (6-12):
- Balanced performance characteristics
- Most common range for general applications
- Good manufacturability
- High C Values (12-22):
- Reduced stress concentration
- Easier to manufacture
- Better for large deflection requirements
Coil Count Engineering
- Active Coils (n):
- Responsible for spring deflection characteristics
- Must be precisely calculated for proper function
- Total Coils (Nt):
- Includes inactive end coils
- Affects solid height and manufacturing process
Material for Compression Springs
Comprehensive Material Selection Guide

| Material Grade | Tensile Strength | Temp Range | Corrosion Resistance | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Music Wire (ASTM A228) | 290-310 ksi | -50°C to 120°C | Moderate | Precision instruments, medical devices |
| 302/304 Stainless | 185-215 ksi | -200°C to 290°C | Excellent | Marine, food processing, chemical |
| 316 Stainless | 170-190 ksi | -200°C to 290°C | Superior | Medical implants, seawater applications |
| Chrome Silicon | 230-260 ksi | -40°C to 220°C | Good | Automotive valves, high-stress applications |
| Inconel X-750 | 160-185 ksi | -250°C to 700°C | Excellent | Aerospace, jet engines |
Material Selection Methodology
- Load Requirements:
- Static vs. dynamic loading conditions
- Fatigue life expectations
- Environmental Factors:
- Temperature extremes
- Chemical exposure
- Humidity/moisture levels
- Regulatory Compliance:
- FDA requirements for medical applications
- RoHS/REACH for consumer products
- MIL-SPEC for defense applications
Precision Manufacturing Process
Step 1: Advanced Coiling Technology
- CNC Coiling Machines:
- ±0.01 mm precision in wire positioning
- Real-time diameter monitoring
- Automatic pitch control
- Cold Winding Process:
- For wires <16 mm diameter
- Maintains material grain structure
- Preserves tensile strength
- Hot Winding Process:
- For heavy-duty springs (16-60 mm)
- Reduces residual stresses
- Enables complex geometries
Step 2: Thermal Treatment Processes
- Stress Relieving:
- 250°C – 300°C for 30-60 minutes
- Reduces internal stresses from forming
- Improves dimensional stability
- Hardening & Tempering:
- Oil quenching for high-carbon steels
- Precipitation hardening for stainless
- Cryogenic treatment for premium grades
Step 3: Surface Enhancement Technologies
| Treatment | Process | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electropolishing | Electrochemical smoothing | Ultra-smooth finish | Medical, food grade |
| Zinc-Nickel Alloy | Electroplating | Superior corrosion resistance | Automotive, marine |
| PTFE Coating | Polymer coating | Dry lubrication | High-cycle applications |
| Black Oxide | Chemical conversion | Aesthetic & mild protection | Consumer products |
Step 4: Rigorous Quality Assurance
- Dimensional Verification:
- Optical comparators for profile checking
- CMM for 3D geometry verification
- Automated vision inspection systems
- Mechanical Testing:
- Computerized load-deflection testing
- Fatigue testing up to 10⁷ cycles
- Salt spray testing per ASTM B117
- Material Certification:
- Spectrochemical analysis
- Microhardness testing
- Grain structure examination
Industrial Applications of Compression Springs
Automotive Sector Solutions
- Engine Valve Springs:
- High-temperature alloys
- Fatigue-resistant designs
- Precision force characteristics
- Suspension Components:
- Progressive rate designs
- Corrosion-protected finishes
- Heavy-duty configurations
Industrial Machinery Applications
- Hydraulic Accumulators:
- High-force designs
- Compact solid heights
- Reliable cycling performance
- Robotic Actuators:
- Miniature precision springs
- Consistent force curves
- Long cycle life
Medical Device Innovations
- Surgical Instrument Springs:
- Biocompatible materials
- Sterilizable designs
- Micro-precision tolerances
- Implantable Mechanisms:
- MRI-compatible materials
- Zero-memory alloys
- Ultra-long fatigue life
Cutting-Edge Electronics
- Connector Contact Springs:
- High-conductivity materials
- Micro-scale geometries
- Precision force requirements
- Haptic Feedback Mechanisms:
- Controlled vibration characteristics
- Miniature form factors
- Silent operation
You can get more information for spring from wiki
ChinaCustomSpring Manufacturing Capabilities
Why Choose ChinaCustomSpring
✅ Uncompromising Quality Standards
- ISO 9001:2015 & IATF 16949 Certified – Rigorous quality management for automotive and industrial applications
- Full Compliance with RoHS, REACH, DFARS – Environmentally safe and defense-compliant materials
- ITAR Registered – Secure manufacturing for aerospace, defense, and sensitive government projects
✅ Advanced Surface Treatment Expertise
- Comprehensive Finishing Options: Zinc plating, nickel coating, phosphating, black oxide, electropolishing
- Specialized Coatings: PTFE coating for friction reduction, epoxy coating for chemical resistance
- Custom Solutions: Passivation for stainless steel, shot peening for enhanced fatigue life
✅ Speed & Scalability
- Rapid Prototyping (72-Hour Turnaround) – Accelerate your product development cycle
- Global Logistics Network with 15 Warehouses – Fast, cost-effective shipping to North America, Europe, and Asia
✅ Expanded Production Capacity
- Wire Diameter Spectrum: 0.05mm (ultra-fine) – 25mm (heavy-duty)
- Tolerance Capabilities: Down to ±0.01mm for mission-critical precision
- Volume Flexibility: From 1-piece prototypes to 10M+ annual production
✅ Streamlined Ordering Process
1. Technical Consultation
- Application Analysis – Optimize spring performance for your specific use case
- Material Selection Guidance – Choose the ideal alloy for corrosion resistance, fatigue life, or extreme temperatures
- Design Optimization – Enhance durability, load capacity, and space efficiency
2. Prototype Development
- 3D Modeling & Simulation – Virtual testing for force curves and stress distribution
- Physical Sample Production – Real-world validation before mass production
- Performance Validation – Load testing, fatigue analysis, and environmental checks
3. Mass Production
-
- Automated Quality Control – 100% inspection for dimensional accuracy and consistency
- Just-in-Time Delivery Options – Reduce inventory costs with scheduled shipments
- Inventory Management Services – Vendor-managed stock programs for high-volume buyers
Request a Detailed Quotation

To receive a customized compression spring solution, please provide:
- Material Specification (Grade and treatment requirements)
- Dimensional Parameters (Wire diameter, coil diameters, free length)
- Performance Requirements (Spring rate, maximum deflection, operating environment)
- Quantity Needs (Prototype, small batch, mass production)
- Special Requirements (Certifications, testing protocols, packaging)
Technical Support: [info@chinacustomspring.com]
Sales Inquiries: [Guswong@188.com]
Complementary Spring Products
- Torsion Springs for rotational force applications
- Extension Springs for tension requirements
- Custom Wire Forms for complex mechanisms
- Belleville Washers for high-load stacking solutions
- Constant Force Springs
- Circlips
Conclusion: Your Trusted Compression Spring Partner
Compression springs represent one of the most versatile and widely used mechanical components across industries. At ChinaCustomSpring, we combine German-engineered production equipment, Japanese-quality standards, and American-style customer service to deliver spring solutions that outperform expectations. Our vertically integrated manufacturing campus allows complete control over every production stage, from raw material selection to final inspection.
Whether you require medical springs, defense components, or high-volume automotive solutions, our team of PhD-level engineers and master spring technicians stands ready to support your project.
Contact our team today for a no-obligation design consultation and spring quotation!