Structural Types of Hot-Formed Spring Ends: Design and Manufacturing Considerations
Introduction
 ChinaCustomSpring is a professional manufacturer specializing in custom-made springs and wire forming, offering precision-engineered solutions for automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Among its core competencies is the production of hot-formed helical compression springs, which are critical for high-load environments due to their superior strength and fatigue resistance.
ChinaCustomSpring is a professional manufacturer specializing in custom-made springs and wire forming, offering precision-engineered solutions for automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Among its core competencies is the production of hot-formed helical compression springs, which are critical for high-load environments due to their superior strength and fatigue resistance.
A crucial aspect of hot-formed spring design is the end structure, which directly impacts load distribution, stability, and fatigue life. This article explores the standard and non-standard end types of hot-formed springs, their manufacturing processes, and industry applications, providing an in-depth technical guide for engineers and designers.
Hot-Formed Spring Manufacturing Overview
Hot-formed springs are typically used when:
-
Wire diameter exceeds 14mm (round) or 10mm (rectangular).
-
High stress resistance and durability are required (e.g., automotive suspension systems).
The manufacturing process follows GB/T 23934 (Technical Specifications for Hot-Formed Helical Compression Springs) and includes:
-
Material Preparation – Cutting, heating, and end shaping.
-
Hot Coiling – Forming at high temperatures (800–950°C).
-
Heat Treatment – Quenching & tempering for enhanced hardness.
-
Finishing – Shot peening, grinding, and anti-corrosion coating.
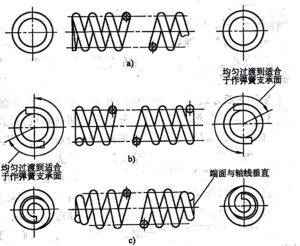
Classification of Hot-Formed Spring End Structures
The end structure determines how the spring interacts with mounting surfaces. The two primary categories are:
1. Standard End Types (GB/T 23934)
Four standardized configurations ensure compatibility with industrial applications:
-
Closed & Ground Ends (Type A) – Fully squared and polished for even load distribution.
-
Closed Ends (Type B) – Squared but unground, cost-effective for moderate loads.
-
Open Ends (Type C) – Unmodified coils, used in dynamic loading.
-
Reduced Diameter Ends (Type D) – Tailored for specific housing fits.
2. Non-Standard End Types
Custom designs are often developed for specialized applications:
(a) Single Closed & Ground End (One Side)
-
Design: One end is squared and ground; the other remains open.
-
Application: Light-duty automotive suspensions (e.g., shock absorbers).
-
Advantage: Reduces manufacturing costs while maintaining partial stability.
(b) Tangential Tail Ends
-
Design: Ends feature a tangent tail (single or double-sided).
-
Application: Heavy-duty vehicle suspensions (e.g., truck leaf spring assist).
-
Advantage: Prevents lateral displacement under cyclic loads.
(c) Non-Ground Reduced Diameter Ends
-
Design: Support coils are tapered without grinding.
-
Application: Mounted springs in suspension systems (e.g., coil-over setups).
-
Advantage: Eliminates post-coiling grinding, enhancing fatigue life.
Key Manufacturing Considerations
1. End Formation Methods
-
Pre-Coiling Flatting (For Furnace-Heated Springs)
-
Ends are flattened before coiling to ensure uniform compression.
-
Post-coiling grinding is avoided, reducing production steps.
-
-
Post-Coiling Grinding (For Resistance-Heated Springs)
-
Maintains uniform cross-section during electric heating.
-
Requires precision grinding to achieve flatness.
-
2. Equipment & Tooling
Hot-forming demands specialized machinery:
-
Cutting: High-speed shearing machines.
-
Heating: Induction or furnace systems (for uniform temperature).
-
Coiling: CNC hot-winding machines with mandrel customization.
-
Finishing: Shot peening (for stress relief) and CNC grinding.
3. Fatigue Resistance Optimization
-
Shot Peening introduces compressive stresses to delay crack propagation.
-
Strong-Pressing (Presetting) improves dimensional stability under load.
Industry Applications
| End Type | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|
| Closed & Ground (Type A) | Precision machinery, hydraulic valves |
| Tangential Tail (Non-Std.) | Commercial vehicle suspensions |
| Reduced Diameter (Type D) | Aerospace landing gear |
Conclusion
The structural design of hot-formed spring ends is pivotal in ensuring load efficiency, longevity, and safety. ChinaCustomSpring leverages advanced manufacturing techniques—from precision coiling to fatigue-enhancing treatments—to deliver springs that meet AS9100, ISO 9001, and automotive OEM standards.
For engineers, selecting the right end type involves balancing:
✔ Functional requirements (load, alignment).
✔ Manufacturing feasibility (cost, post-processing).
✔ Fatigue performance (shot peening, heat treatment).
As industries demand higher-performance springs, innovations in non-ground ends and tailored tang designs are becoming increasingly critical.
Partner with ChinaCustomSpring for bespoke spring solutions—where precision meets durability.