Torsion Springs

Torsion springs are mainly used for compression and energy storage in mechanical engineering, and can also be used as elastic links in transmission systems. The cross-section of the material used for torsion spring is mostly circular, followed by rectangular, and there are also elliptical and trapezoidal ones.
Characteristics of torsion springs
Basic geometric parameters and characteristics of torsion springs
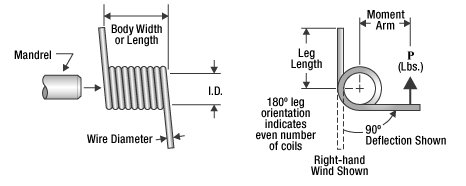
The following figure shows the basic geometric parameters and characteristic relationships of torsion springs.
T1, T2, …, Tn are working torques, and the corresponding torsional deformation angles are φ1, φ2, …, φn. Take the test torque that reaches the test stress σs as Ts, and the corresponding torsional deformation angle under the test torque as φs. In order to ensure the torque under the specified torsional deformation angle, T and φ should be between 20% and 80% of the test torque T and the deformation angle φ under the test torque, respectively.
Due to the structural shape of the spring end, the friction between the spring and the guide rod, etc., which affect the characteristics of the spring, no characteristic requirements are specified unless there is a special need. If the spring characteristic requirements are specified, a spring with a gap between the spring coils should be used, and the torque at the specified torsional deformation angle should be used for assessment.
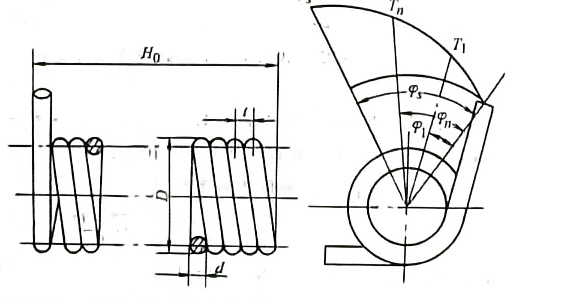
Basic geometric parameters and characteristic relationships of cylindrical helical torsion springs
Test torque of torsion springs and deformation angle under test torque
Test torque T is the maximum torque allowed by the spring, and its value can be calculated as follows:
Ts=(πd3/32) σs
Where
- d: spring material diameter
- σs: test bending stress
For springs of Class 1 and Class II loads, in some cases, σs = (1.1~1.3) [σ], or Ts = (1.1~1.3) T, can be taken. However, the value must not exceed the maximum test bending stress value, or its corresponding maximum test torque
Structural design of torsion springs
Structural type of torsion springs
(1) Type of spring
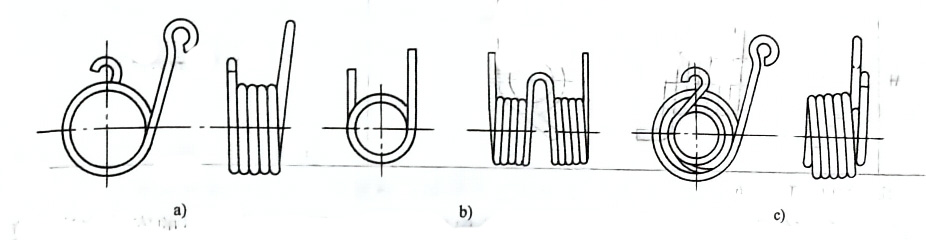
The types of torsion springs are shown in the figure below.
- Figure a is a commonly used ordinary torsion spring:
- Figure b is a parallel double torsion spring:
- Figure c is a straight double torsion spring.
Types of helical torsion springs
The parallel double torsion spring shown in Figure b is a spring material wound in opposite directions on the same mandrel with the same number of circles. The middle of the two springs is a buckle ring, and the two ends are fulcrums for applying torque. The torsional stiffness of each spring is equivalent to twice the total length of the two springs when used as a single spring.
The stiffness of the parallel double torsion spring is 4 times that of its single spring, and the deformation is 1/4 of its single spring. Therefore, this parallel double torsion spring has high efficiency.
Figure C is an inner and outer in-line double torsion spring. Compared with the torsion spring of the same outer diameter, this structure can almost get twice the deformation, that is, nearly twice the deformation angle. Therefore, this spring is suitable for occasions where the space is small and a large deformation angle is required, or where the torque acts on nearly the same plane.
In addition, torsion springs are divided into two types: no spacing and spacing. The friction of the no-spacing spring will affect the working characteristic line because the coils are in close contact with each other, but it is still widely used because it is easy to manufacture.
Torsion springs with spacing are used in occasions with high precision requirements, and the spacing between the coils is generally δ≈0.5mm.
Structural types of torsion springs
Outer arm torsion spring
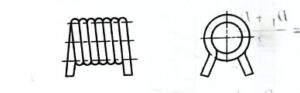
Inner arm torsion spring
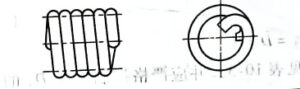
Center arm torsion spring
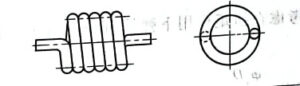
Parallel double torsion spring
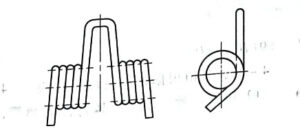
Straight arm torsion spring
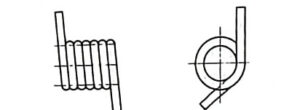
Single arm bending torsion spring
End structure of spring
There are many end structure types of torsion springs, which can be selected according to different installation methods and use conditions. There are outer arm type, inner arm type and center arm type.
Calculation of structural parameters of torsion spring
1.Spring material diameter
The selected value of spring material diameter should comply with the material diameter specification.
2.Spring coil diameter
- Spring middle diameter
- Spring inner diameter:
- Spring outer diameter:
The spring middle diameter D shall comply with the provisions of GB/T1358, and the deviation of the outer diameter D2 shall be strictly controlled.
In order to avoid the spring from clamping the guide rod after being subjected to torque, the reduction of the spring diameter under the action of torque should be considered.
3.Spring winding ratio
4.Number of spring coils
The effective number of spring coils, for springs that need to be evaluated for characteristics, generally has no less than three effective working coils.
5.Spring free angle
The free angle is the angle between the two torsion arms when there is no load and can be determined as needed.
For springs with characteristic requirements, the free angle is not required to be tested.
6.Spring pitch
7.Spring free length
8.Spring helix angle and direction of rotation
When there are no special requirements, the spring coil is generally right-handed.
9.Spring material unfolded length
For specific calculation method formula and other information, please refer to
Calculation formula of cylindrical helical torsion spring
Installation and structure example of cylindrical spiral torsion spring
Torsion Springs Manufacturer in China
We take pride in being a leading custom-made torsion springs manufacturer in China. With years of experience and a commitment to quality, we have earned a reputation for providing high-quality springs that meet the unique requirements of our clients.
As a custom-made torsion springs manufacturer, we understand the importance of precision and customization. We work closely with our clients to fully grasp their specific needs and design springs that align perfectly with their applications. Our team of skilled engineers utilizes advanced software and technology to create detailed designs, ensuring accuracy and reliability in every spring we produce.
- Material:Carbon steel,alloy spring steel,music wire steel,and stainless steel,iron,plated steel,alloy steel,bronze,red bronze,phosphor
copper,and beryllium copper;etc - Surface Treament:Black oxide,Zinc/Nicke/Chrome plating,power coating,oiled to prevent rust,passivate,etc.
- Wire diameter:0.1mm- 12mm
As the demand for torsion springs continues to grow across various industries, finding a professional manufacturer to meet your specific requirements is of paramount importance.We are professional manufacturer custom-made spring in China.Our customization capabilities, use of premium materials, and cost-effective solutions make us reliable partners across various industries.
What Distinguishes Torsion Springs?
One distinctive characteristic of torsion springs is their ability to store and release energy through a twisting motion, unlike other types of springs that typically operate through compression or extension. This twisting action enables torsion springs to produce high torque or rotational force, making them ideal for applications that require a rotating force, such as door hinges, garage doors, and various machinery.
Another notable feature of torsion springs is their adaptability. By altering their design parameters, such as wire diameter, outer diameter, and the number of coils, their properties can be adjusted. This high degree of customization and versatility allows torsion springs to be tailored to meet the unique needs of different applications. Furthermore, torsion springs are renowned for their robustness and longevity, as they can withstand repeated twisting and untwisting without suffering from fatigue failure. As a result, they are a dependable and cost-effective option for numerous industrial and consumer applications.
Custom Torsion Springs Manufacturing
ChinaCustomSpring specializes in creating custom torsion springs tailored to your exact specifications for any project you have in mind. Our team provides expert engineering support throughout the entire process, from design to production. We offer a vast array of material and finish options to perfectly suit your torsion spring design application.
In addition to our manufacturing services, we can also assist with CAD-based torsion spring design, governmental and industrial regulatory compliance, and prototype development through large-scale production runs. ChinaCustomSpring boasts advanced manufacturing capabilities and a wide range of options for your torsion spring needs, including advanced quality control systems, compliance expertise with regulations such as RoHS, REACH, and DFARS, CAD-assisted product design, in-house prototype production services, and a global supply chain network.
To get started on your custom spring project, simply request a quote today or reach out to a ChinaCustomSpring engineer for design assistance or to answer any questions you may have.
Material of Torsion Springs
As a professional manufacturer, we handle many types of material for torsion springs, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, music wire and so on.
You also can check more details from following table.
| Standard No | standard | Brand | Diameter specification (mm) | shear | Recommended hardness HRC | Recommended | performance |
| name | Modulus G (MPa) | Temperature ℃ | |||||
| GB | Carbon spring steel wire | 25~80 | Grade B: 0.08~13.0 | 79000 | – | -40~130 | High strength, good performance.Class B, C and D are used for low, medium and high stress springs respectively |
| 4357 | 40Mn~70Mn | Grade C: 0.08~13.0 | |||||
| Level D: 0.08~6.0 | |||||||
| GB | Piano wire | 60~80 | Group G1: 0.08 ~ 6.0 | 79000 | – | -40~130 | High strength and good toughness.For important small springs, Group G2 is stronger than Group G1, and Group F is mainly used for valve springs |
| 4358 | T8MnA~T9A | Group G2: 0.08 ~ 6.0 | |||||
| 60Mn~70Mn | Group F: 2.0 ~ 5.0 | ||||||
| GB | Oil quenched and tempered carbon spring steel wire for valves | 65Mn | 2.0~6.0 | 79000 | – | -40~150 | High strength, good performance.For internal combustion engine valve spring or similar spring |
| 4359 | 70 | ||||||
| GB 4360 | Oil quenched and tempered carbon spring steel wire | 55、60、60Mn、65、65Mn、70、70Mn、75、80 | Class A, Class B | 79000 | – | -40~150 | High strength, good performance.It is applicable to springs for common machinery.Class B has higher strength than Class A |
| 2.0~12.0 | |||||||
| GB | Oil quenched and tempered silicon manganese spring steel wire | 60Si2MnA | Class A, B, C | 79000 | – | -40~200 | High strength and good elasticity.Easy to decarburize, used for high load springs.Types A and B are used for general purpose springs, and types B and C are used for automobile suspension springs |
| 4361 | 2.0~14.0 | ||||||
| GB | Oil quenched and tempered chromium silicon spring steel wire for valves | 55CrSi | 1.6~8.0 | 79000 | – | -40~250 | With strong fatigue strength, it is used for high stress internal combustion engine valve springs or other similar springs at higher operating temperatures |
| 4362 | |||||||
| GB | Oil quenched and tempered chrome vanadium spring steel wire for valves | 50CrVA | 1.0~10.0 | 79000 | – | -40~210 | ditto |
| 2271 | |||||||
| GB | Silicon manganese spring steel wire | 60Si2MnA | 1.0~12.0 | 79000 | 45~50 | -40~200 | High strength, good elasticity and easy decarburization.Larger springs for general machinery |
| 5218 | 65Si2MnWA | ||||||
| 70SI2MnA | |||||||
| GB | Chromium vanadium spring steel wire | 50CrVA | 0.8~12.0 | 79000 | 45~50 | -40~210 | Stable strength performance at high temperature, used for springs at high temperature, such as valve springs of internal combustion engines |
| 5219 | |||||||
| GB | Chromium vanadium spring steel wire for valves | 50CrVA | 0.5~12.0 | 79000 | 45~50 | -40~210 | ditto |
| 5220 | |||||||
| GB | Chromium silicon spring steel wire | 55CrSiA | 0.8~6.0 | 79000 | 45~50 | -40~250 | Stable strength performance at high temperature, used for high stress spring at high temperature |
| 5221 | |||||||
| YB(T) | Stainless steel wire for spring | Group A: | whole | 71000 | -200~300 | Corrosion resistant, high and low temperature resistant, small spring used for working under corrosion or high and low temperature conditions | |
| 11 | 1Cr18Ni9、 | 0.8~12.0 | |||||
| 0Cr19Ni10、 | |||||||
| 0Cr17NI12Mo2 | |||||||
| Group B: 1Cr18Ni9 | |||||||
| 0Cr18Ni10 | |||||||
| Group C: 0Cr17Ni8Al | |||||||
| GB | Silicon bronze wire | QSi3-1 | 0.1~6.0 | 41000 | HB90~100 | -40~120 | It has high corrosion resistance and antimagnetic performance.Elastic elements for machinery and instruments |
| 3121 | |||||||
| GB | Tin bronze wire | QSn4-3 | 0.1~6.0 | 40000 | HB90~100 | -250~120 | It has high wear resistance, corrosion resistance and antimagnetic performance.Elastic elements for machinery and instruments |
| 3124 | QSN6.5-0.1 | ||||||
| QSn6.5-0.4 | |||||||
| QSn7-0.2 | |||||||
| GB | Beryllium bronze wire | QBe2 | 0.03~6.0 | 44000 | 37~40 | -200~120 | It has high wear resistance, corrosion resistance, antimagnetism and conductivity.Precision elastic elements for machinery and instruments |
| 3134 | |||||||
| GB | Hot rolled spring steel | 65Mn | 5~80 | 78000 | 45~50 | -40~120 | Good elasticity, used for ordinary mechanical springs |
| 1222 | 55Si2Mn | 5~80 | 78000 | 45~50 | -40~200 | With high fatigue strength and good elasticity, it is widely used in springs for various machines, vehicles, etc | |
| 55Si2Mn8 | |||||||
| 60Si2Mn | |||||||
| 60Si2MnA | |||||||
| 55CrMnA | 5~80 | 78000 | 47~52 | -40~250 | Good elasticity, high temperature resistance, used for larger springs bearing heavy loads | ||
| 60CrMnA | |||||||
| 50CrVA | 5~80 | 78000 | 45~50 | -40~210 | High fatigue strength, high temperature resistance.For larger springs at higher operating temperatures | ||
Design Considerations for Torsion Springs
When designing with torsion springs, there are several key factors to take into account. Here are some important design considerations for torsion springs in your application:
- Specify torsion spring loads at a fixed angular position, rather than at a fixed deflection from the free position.
- Torque measurements for torsion springs can be challenging and may yield inconsistent results.
- Consider the potential for inner diameter reduction and binding in your application.
- To minimize hysteresis (load loss), design torsion springs with space between adjacent coils to reduce frictional losses.
- Always load a torsion spring in a direction that causes its body diameter to decrease, as this direction is favorable for residual forming stresses. Loading in the opposite direction is unfavorable.
- Maintain clearance between the mandrel and the torsion spring at all times to prevent binding. The ideal mandrel size is equal to or slightly less than 90% of the inside diameter when the spring is fully deflected. Avoid using mandrels significantly smaller than 90% to prevent buckling during large deflections.
- Most torsion springs are close wound, so the body length will increase when deflected in the direction that reduces the coil diameter. Consider this increase in tight housing designs.
- Always specify the direction of wind for a torsion spring. You can determine the direction of wind by holding the spring in your hand with your fingers around the outside of the body and your thumb pointing up. If the last coil ends in the same direction as your fingers, that is the hand (direction of wind) of the spring. Torsion springs can have a right-hand, left-hand, or double torsion wind. Good design practice dictates using torsion springs in the direction that winds the coil.”
Production equipment
The main production equipment: digital control multi-functional computer spring machine, automatic spring coiling machine, spring grinding machine, heat treatment equipment, large coil spring production line, quality testing instrument.
Torque spring is a high-precision spring accessory that cannot be processed at 1800 degrees using ordinary spring machines. Generally, universal spring machines are used both domestically and internationally to produce torque springs, with high accuracy. Universal springs can achieve forming and positioning of different angles and shapes. It is a relatively universal CNC universal machine and fully automatic production equipment
The main functions of the universal spring machine


A widely used elastic component in the spring machine and electronics industry. Springs can generate significant elastic deformation when subjected to load, converting mechanical work or kinetic energy into deformation energy. After unloading, the deformation of the spring disappears and returns to its original state, converting deformation energy into mechanical work or kinetic energy.
- In a universal spring machine, springs control the movement of machinery, such as valve springs in internal combustion engines and control springs in clutches.
- The spring in a universal spring machine absorbs vibration and impact energy, such as buffer springs under cars and train carriages, and vibration absorbing springs in couplings.
- In a universal spring machine, springs store and output energy as power, such as clock springs and springs in firearms.
- In a universal spring machine, the spring is used as a force measuring element, such as a force measuring device or a spring in a spring scale. The ratio of the load to deformation of the spring is called spring stiffness, and the greater the stiffness, the harder the spring