Stability, Strength and Resonance Check of Coil Springs
(1) Compression spring stability check
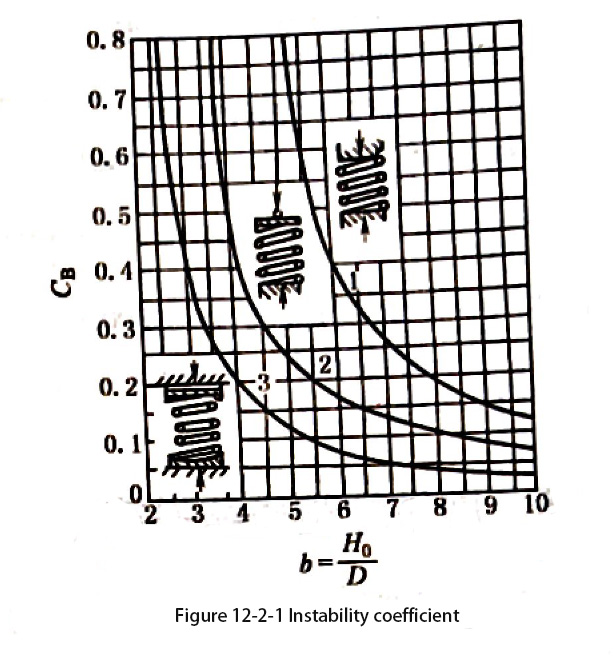
Compression spring with a larger height-diameter ratio b will bend laterally and lose its stability when the axial load reaches a certain value. In order to ensure stable use, the height-diameter ratio b=H/D should meet the following requirements:
fixed at both ends b≤5.3
One end fixed, the other end rotated b≤3.7
Rotation at both ends b≤2.6
When the height-diameter ratio b is greater than the above value, check and calculate according to the following formula
Pc=Cb P’Ho>Pn
in the formula, Pc——Critical load of spring, N;
Cb——Instability coefficient, get it from Figure 12-2-1;
P’——spring stiffness, N/mm;
Pn——Maximum working load, N.
If the above formula is not satisfied, the parameters should be reselected, the b value should be changed, and Pc should be increased. value to ensure the stability of the spring. If the design structure is limited and the parameters cannot be changed, guide rods or guide sleeves should be provided. Check the clearance (diameter difference) between the guide rod (guide sleeve) and the spring according to Table 12-2-15.
In order to ensure the characteristics of the spring, the height-diameter ratio of the spring should be greater than 0.4.
Table 12-2-15 Clearance value of guide rod, guide bush and inner (outer) diameter of spring mm
| Spring diameter D | ≤5 | >5~10 | >10~18 | >18~30 | >30~50 | >50~80 | >80~120 | >120~150 |
| Gap | 0.5~1 | 1~2 | 2~3 | 3~4 | 4~5 | 5~6 | 6~7 | 7~8 |
(2) Strength check
Fatigue strength check shall be carried out for important springs (types I and II) subjected to cyclic loads; static strength check shall be carried out if the number of cyclic loads is small or the variation of cyclic loads is small. When the two are not easily distinguishable, the verification of the two strengths should be carried out at the same time.
a. Fatigue strength, as follows:
Safety factor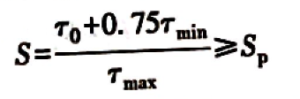
τ0 ——Shear fatigue strength of spring under pulsating cyclic load, for high-quality steel wire, stainless steel wire, beryllium bronze and silicon bronze, refer to Table 12-2-16;
τmax—— maximum shear stress due to maximum working load,
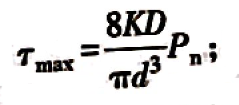
τmin——Minimum shear stress due to minimum working load,
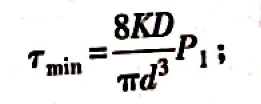
Sp——allowable safety factor, when the design calculation and material test accuracy of the spring is high, take Sp= 1.3~1.7; when the accuracy is low, take Sp = 1.8~2.2.
Table 12-2-16 Shear strength under cyclic loading of high quality steel wire, stainless steel wire, beryllium bronze and silicon bronze τ0
| The number of cyclic load actions N | 104 | 105 | 106 | 107 |
| τ0 | 0.45σb ① | 0.35σb | 0.33σb | 0.30σb |
①For silicon bronze and stainless steel wire, this value is 0.35σb.
b. Static strength, calculated as follows:
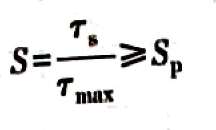
In this formula,τs——the yield limit of the spring material;
Sp——The allowable safety factor is the same as the selection of fatigue strength check.
(3) Resonance check
For springs subjected to cyclic loads in high-speed operation, resonance checking is required. Its check formula is
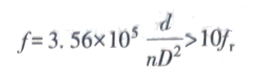
in the formula
f—natural frequency of spring, Hz:
fr—Forced mechanical vibration frequency,Hz:
d—spring material diameter, mm;
D—spring diameter, mm;
n—the effective coils of the spring.
For the damping spring, check the following formula
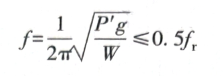
In the formula
g—gravity acceleration, g=9800mm/s2;
P’-spring stiffness, N/mm;
W—load, N.






